RNDR, AKT, IONET: The Complete Guide on AI Compute Networks
Comprehensive ecosystem breakdown of different GPU networks in Web 3
This post was brought to you by Yield Guild Games (YGG). YGG is a web3 guild protocol that enables players and gaming guilds to find their community, discover games and level up together. Its mission is to become the leading community-based user acquisition platform in web3 gaming through fun quests that help players build their onchain reputation.
Find out more at: https://investors.yieldguild.io/
Introduction
The convergence of Crypto x AI ecosystem is no more a dream. The ecosystem has experienced some amazing growth in the last few months. Decentralised cloud computing has been one of the sub sectors that has had the highest development and performed well.
Imagine harnessing unused computing power to make high-performance computing accessible to everyone - this is the promise of decentralized compute providers.
There are many players in this space including the big giants like Render and Akash, along with emerging projects like IO, Aethir, GPU.net, and NodeAI.
The decentralized compute model aims to address high costs, security concerns, and scalability issues inherent in centralized systems. By tapping into idle computational resources, these projects offer innovative solutions to these challenges.
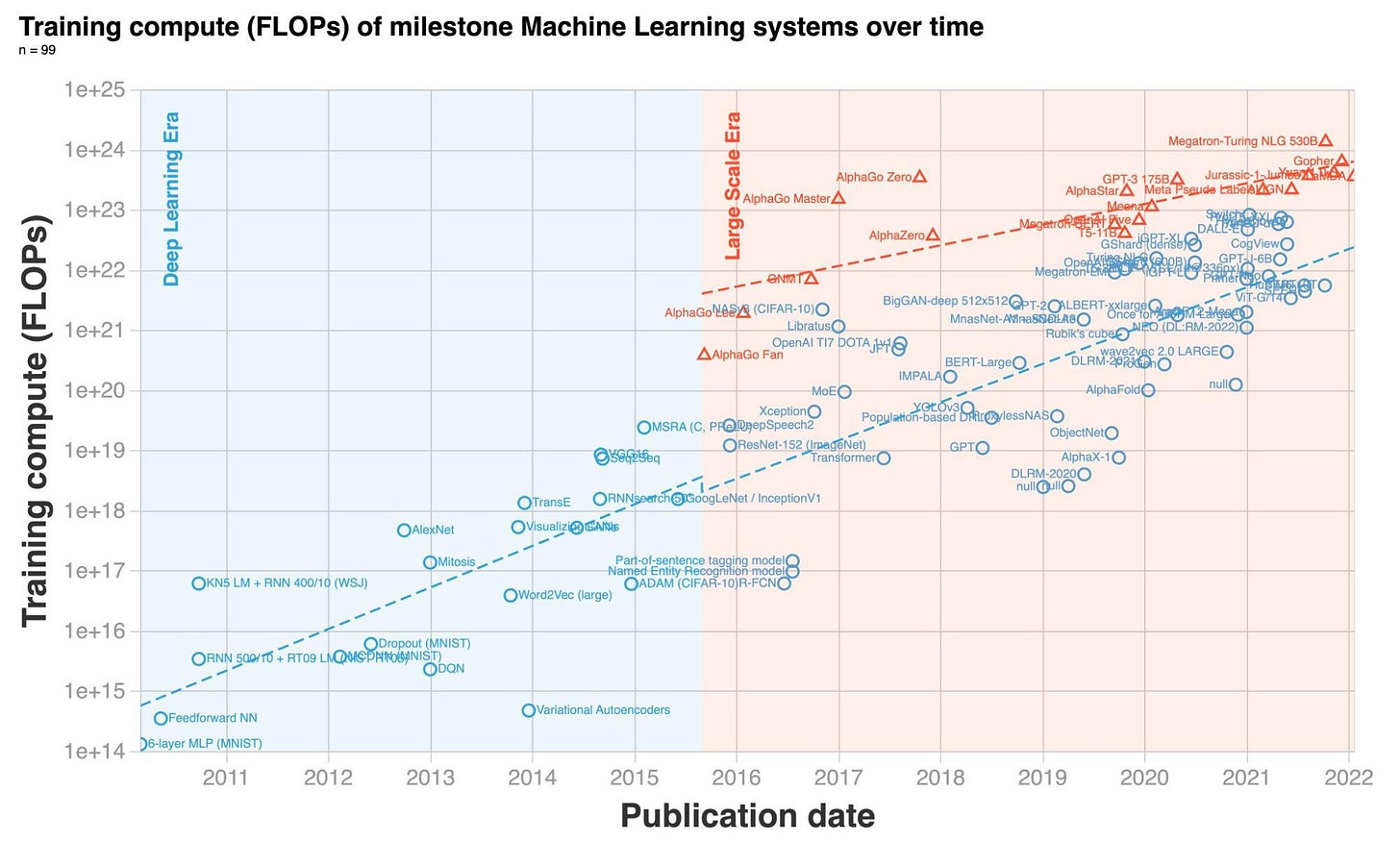
NVIDIA has been a leader in AI hardware, significantly contributing to AI's growth with its powerful GPUs. However, the real surge in computational power demand came with the rise of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT.
ChatGPT, which reached 100 million users in just two months, highlights the need for scalable and efficient compute solutions.
Training advanced models like GPT-4, which cost over $100 million, underscores the immense compute demands. Elon Musk also emphasized the "insane" compute requirements for AI, far exceeding typical web applications.
This is where the need for decentralised compute networks becomes crucial. These platforms aim to offer a secondary market for leasing excess compute capacity. The focus of this approach is to democratise access to state-of-the-art GPUs, addressing the scarcity of these critical resources and also helps utilise under-utilised GPUs to their full potential.
By leveraging underutilized computing resources and encouraging a more collaborative model, these providers aim to overcome the significant challenges faced by centralized counterparts like Google, AWS and Orcale to name a few.
Several catalysts have fueled the rise of decentralized AI, including the launch of projects like IO.net, node sale of Aethir Cloud and positive market responses to NVIDIA's recent revenue numbers. A lot of projects have also been being funded in the broader crypto x AI space.
Today’s let explore and understand more about this decentralised compute network / marketplace better - the players, the problems and what are the exciting new projects coming up as well.
What does compute even mean?
In AI, compute power refers to the capacity of computers or networks to process large datasets, execute complex algorithms, and perform tasks necessary for training and running AI models.
It measures how quickly and efficiently these systems handle AI workloads, which is crucial for various cycles in AI development lifecycle.
Compute power is essential for many aspects such as:
for training deep learning models that require processing vast amounts of data through numerous iterations like image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition
enabling models to make quick predictions and decisions based on new data, essential for applications like autonomous driving, real-time language translation, and interactive AI assistants
allowing researchers and developers to experiment with and optimize complex algorithms, focusing on research & innovation
running simulations for training AI agents in reinforcement learning environments like gaming and robotics
developing generative models that can interact and create new content, such as GPT-4 for text generation or GPT-4o for image and video synthesis.
Types of compute resources in AI include:
CPUs (Central Processing Units): General-purpose processing tasks.
GPUs (Graphics Processing Units): Parallel processing ideal for training deep learning models.
TPUs (Tensor Processing Units): Designed by Google to accelerate machine learning workloads.
ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits): Custom-designed chips optimized for specific AI tasks, offering high efficiency and performance.
The tech supporting AI compute power includes parallel processing architectures like GPUs and TPUs, high-performance storage solutions such as SSDs and NVMe drives, and advanced networking with high-speed networks and interconnects.
These technologies enable efficient data transfer between compute resources, supporting large-scale distributed AI training.
In AI/ ML, compute power is used for:
Training models: Extensive data processing and optimization to improve model accuracy.
Inference: Applying the model to new data for real-time or batch processing predictions.
Data handling: Managing, cleaning, and preparing large datasets for training.
Model development: Facilitating the iterative design, testing, and refinement of AI models to enhance their capabilities and performance.
By leveraging these resources, developers & companies are really working on pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved.
Centralized vs Decentralized Compute Providers
Centralized cloud providers like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft offer remote computing and storage through their data centers. These companies maintain vast infrastructure but require users to trust them with data privacy and security, making them vulnerable to malware, attacks, and data breaches.

Decentralized AI compute providers like Aethir Cloud, Render Network, and io.net use blockchain and peer-to-peer networks for distributed computing. This model aims to improve security, privacy, and data control, reducing risks of data failures and outages. They are ideal for early-stage tech companies and researchers priced out of centralized clouds.
However, decentralized providers face challenges:
Excess supply over demand complicates resource utilization.
Regulatory hurdles.
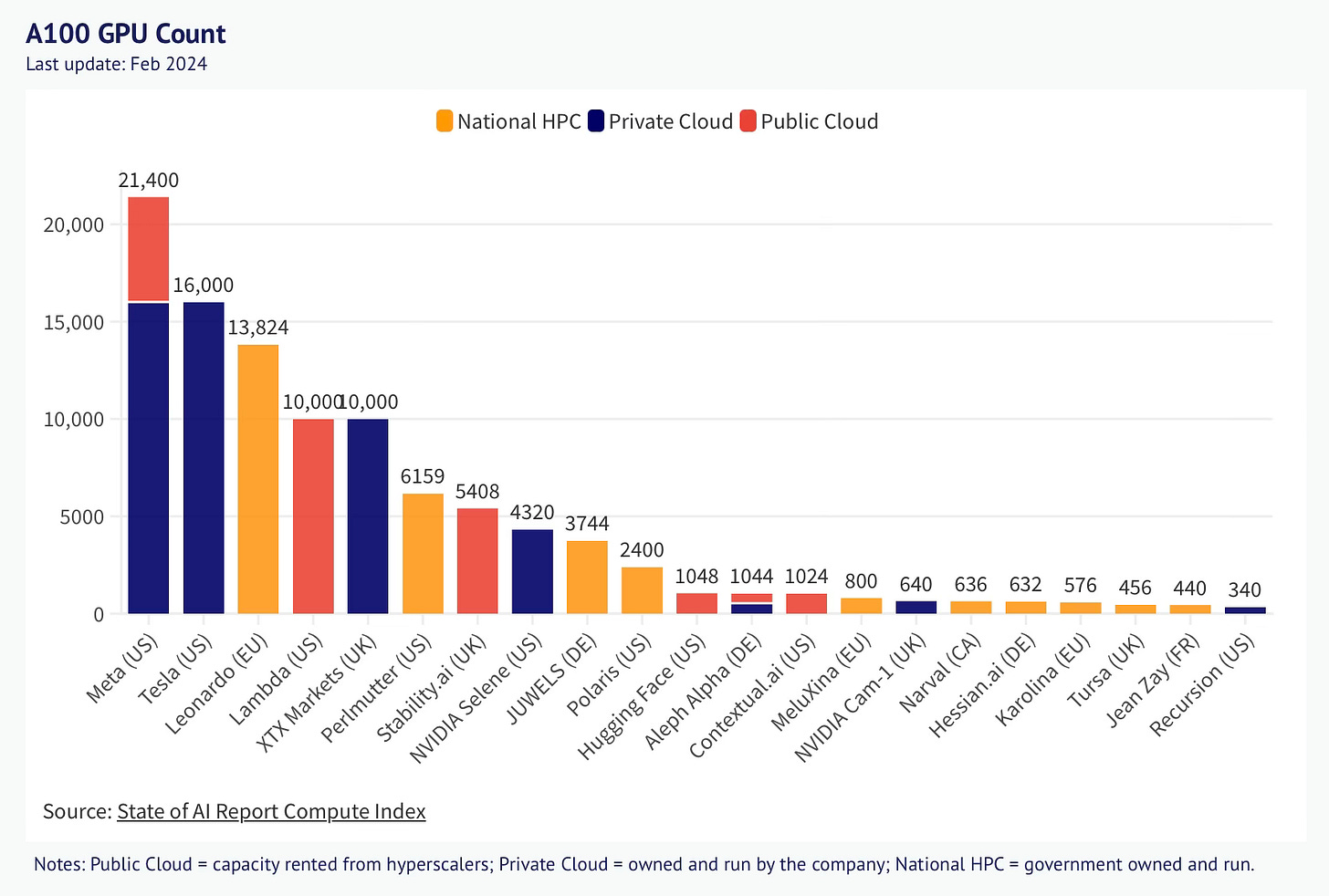
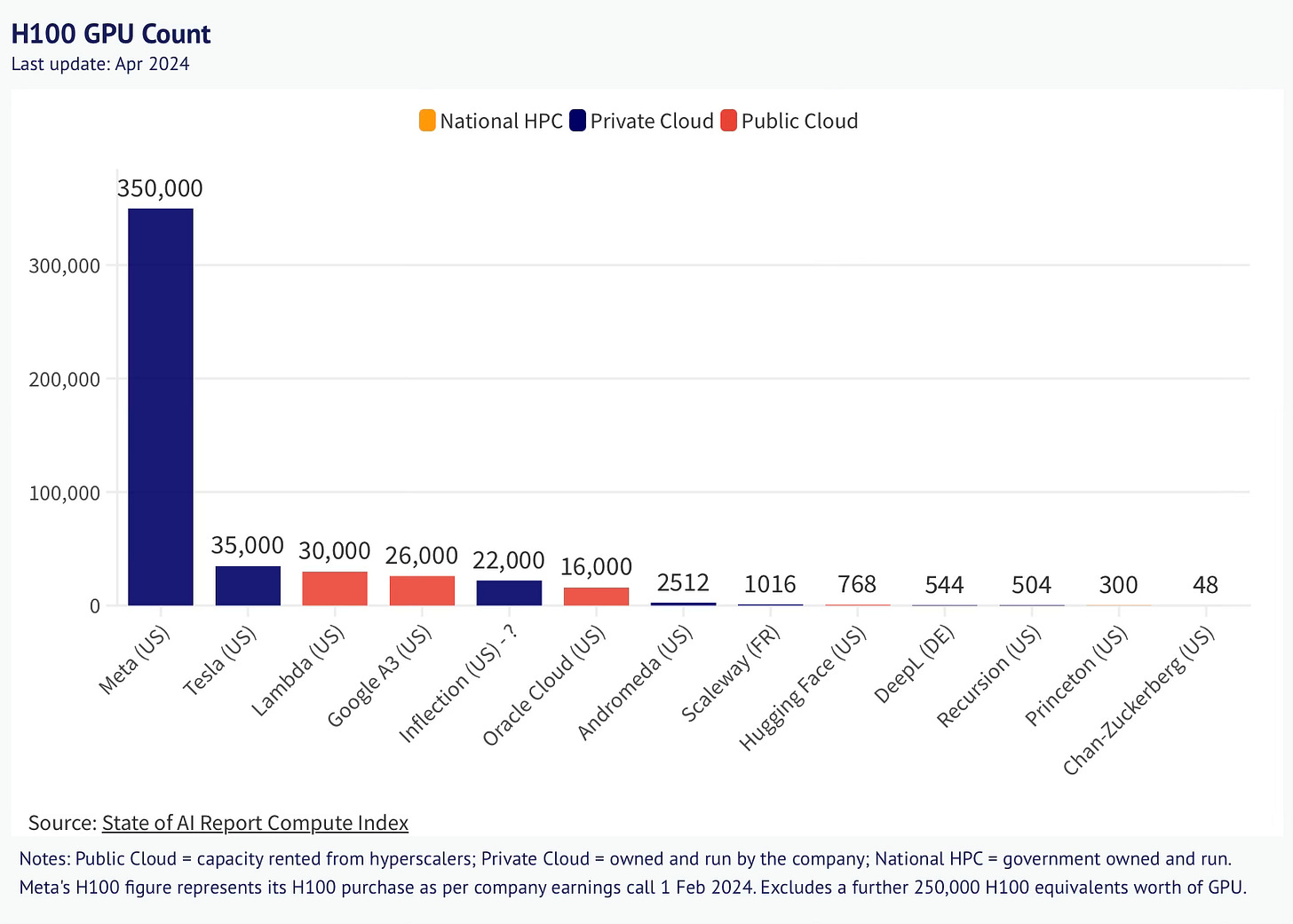
Limited access to high-quality GPUs like NVIDIA's H100s, as manufacturers prioritize giivng allocations to centralized providers.
Despite their potential for faster, cheaper, and more efficient large-scale computing, decentralized providers are not yet the first choice for large companies and governments. Addressing these challenges is crucial for these networks to compete with centralized providers.
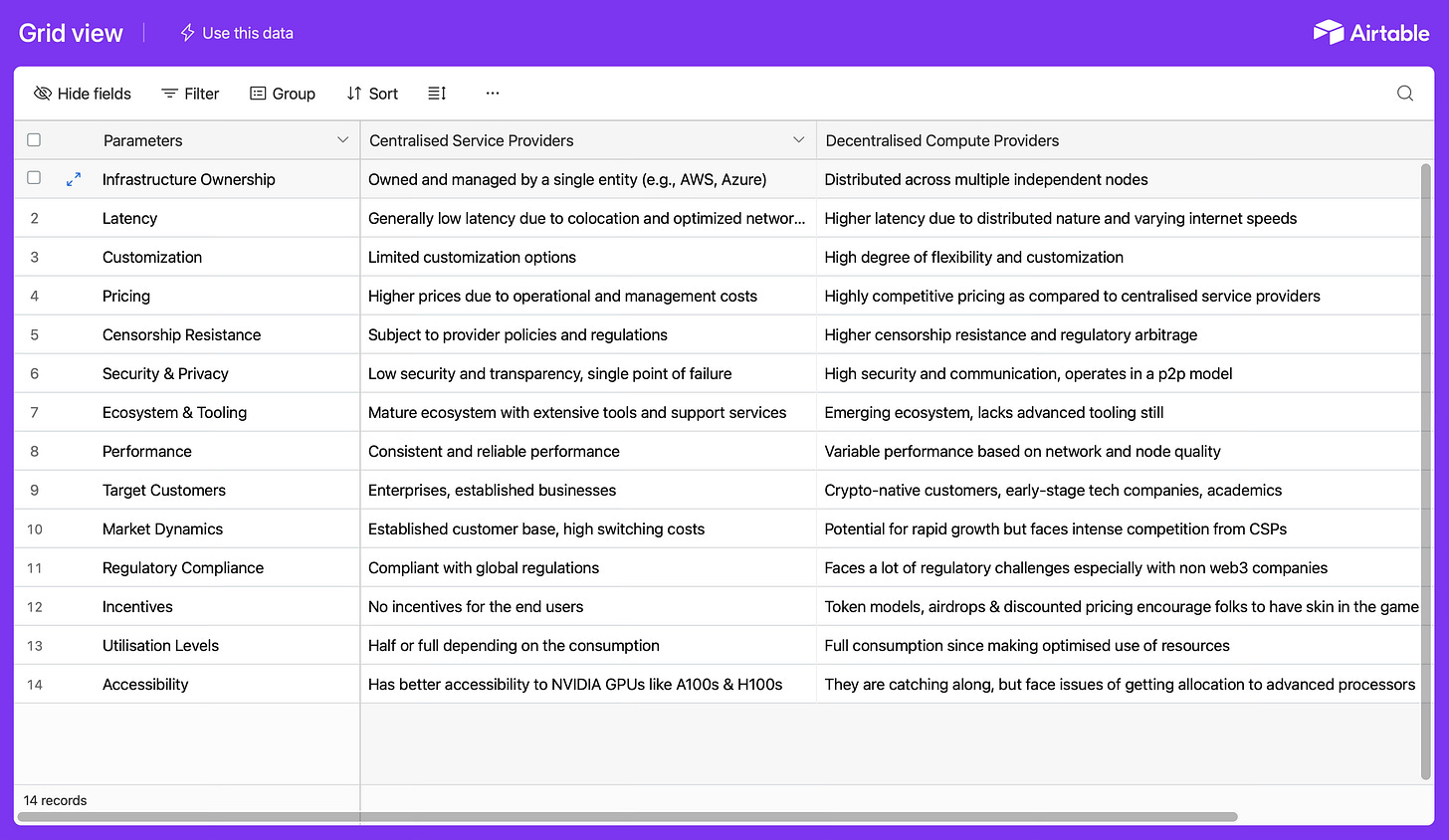
Here's a competitive benchmark comparing centralized and decentralized compute providers.
Catalysts for Growth of the Space
The crypto x AI ecosystem is booming, driven by key catalysts. Aethir Cloud's recent node sale exemplifies this. On March 20, 2024, Aethir launched 100,000 nodes at $500 each. In the first hour, 8,900 participants bought 50,000 nodes, raising $65 million. This success highlights strong demand for decentralized cloud computing.
The IO token launch for io.net’s decentralized AI compute ecosystem is another major driver. Despite a Sybil attack, io.net's resilience and expansion show the potential of decentralized AI platforms. The IO token will facilitate transactions and incentivize network participation.
Investment in AI-related Web3 projects surged to $298 million in 2023, doubling the total funding from 2016 to 2022. Notable rounds include MyShell's $11 million Pre-A and io.net's $30 million Series A, fueling innovation across the crypto x AI landscape.
AI-related tokens outperformed major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum in 2023. Projects like Bittensor, Akash, Render, Fetch, AIOZ, NodeAI, and Ocean Protocol lead the market, showing growing demand for AI compute resources.
NVIDIA's Q1 FY25 revenue hit $26.0 billion, driven by data center growth, underscoring the need for advanced infrastructure to meet escalating AI compute requirements.
These catalysts show the dynamic evolution of the crypto x AI ecosystem, driven by investment, technology advances, and market confidence. As the ecosystem matures, these developments will shape the future of AI and blockchain integration.
AI has dominated the market and mind share over the last 12 months, according to Kaito.

Key Players In The Space
This section focuses on key players operating in this decentralised compute space like Akash, Aethir, IO and Render Network.
We'll look at their approaches, strengths, and the impact they’ve created and the product they’re building.
Let’s get started!
Akash Network
Akash Network is building an open-source marketplace to connect underutilized GPU supply with enterprises needing high-performance compute.
Often described as the "Airbnb" for GPU compute, Akash focuses on providing scalable, enterprise-grade GPU solutions.
Unique Selling Points
Targets enterprises with computational needs by providing high-quality GPU solutions.
Post GPU mainnet launch, onboarded 150-200 GPUs with 50-70% utilization, generating $500K-1M GMV annually.
Offers cost-effective alternatives to traditional cloud providers by leveraging underutilized resources.
User Experience Enhancements
Started off in the Cosmos ecosystem and accepted payments only in $AKT
But over a period of time has evolved to support USDC payments, integrated with Metamask to reduce friction and improve onboarding.
$AKT Tokenomics

Circulation: ~60% as of May 2024.
Inflation Rate: 13% annually, increased from an initial 8%.
Economics:
4% fee for payments in AKT
20% take rate for USDC payments.

How does the $AKT Token Accrues Value?
Staking $AKT secures the network, deterring malicious activities and rewarding participants.
$AKT is used for transactions within the Akash marketplace, integrating it into core operations.
Staking rewards in $AKT encourage active participation and network security.
$AKT serves as a reserve currency within Cosmos' multi-currency, multi-chain ecosystem.
Recent listing on exchanges like Upbit boosts demand and adoption
Role of $AKT in the Akash Ecosystem
Staking: Required for compute resource providers, securing the network.
Governance: AKT holders can propose and vote on network upgrades and changes.
Transactions: Used for payments and accessing services on the platform.
Incentives: Rewards participants for contributing to the network, promoting active engagement.
As per Modular Capital’s thesis, here’s a projection on how Akash might perform over time.
Render Network
Render Network is a decentralized platform that leverages blockchain technology to transform 3D content rendering.
Users can monetize idle GPU resources for tasks like rendering visual effects, creating NFTs, and integrating live action with 3D environments.
The target audience and focus is on creating a collaborative community of 3D artists, creators and engineers.
What Makes Render Unique?
Uses idle GPU power for rendering 3D graphics and visual effects for creators
Adjusts rates based on job complexity, urgency, and available resources.
Optimizes job assignments based on GPU type, capacity, location, and reputation.
Uses Proof-of-Render to verify outputs, ensuring security without centralized validation.
Makes high-quality rendering services available globally to a wide audience.
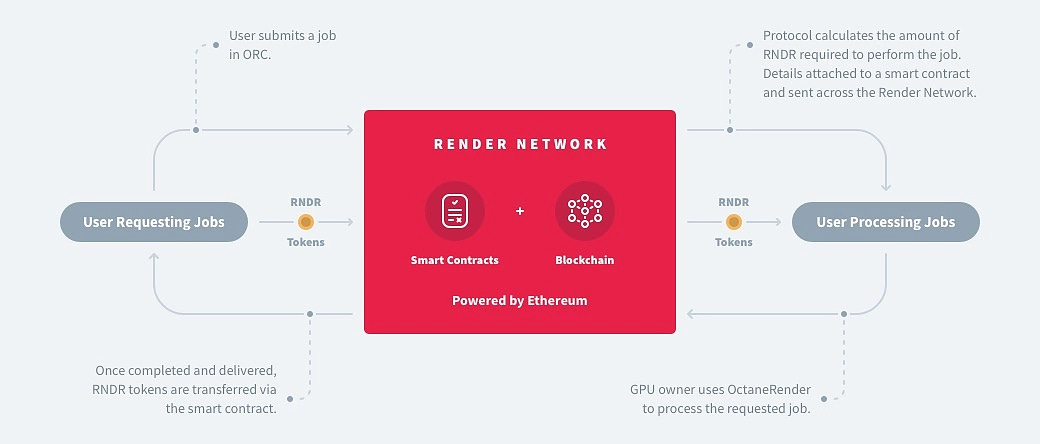
Tokenomics of RNDR

Total Supply: 536,870,912 RNDR tokens.
Allocation: 25% for fundraisers, 10% for project reserves.
Primary Payment: RNDR is used for rendering jobs on the platform.
Governance: RNDR holders participate in the Render DAO.
Staking: Users can stake RNDR to earn rewards and participate in network activities.
How does the $RNDR Token Accrues Value?
Payment: Used for rendering jobs, driving direct demand.
Governance: Holders participate in decision-making through the Render DAO.
Scarcity: Limited supply increases value over time as demand grows.
Staking Rewards: Incentivizes active engagement and network participation.
Here’s a great flowchart to understand this better
IO.net
IO.net is one of the most recent GPU networks that has been the talk of the town, operating on Solana. Part of the attention, unfortunately, comes from allegations on Twitter regarding the veracity of Ionet’s claims and exaggerations over earnings. The section below will only cover Ionet’s proposed offerings in order to highlight differences in positioning between different networks.
Ionet aggregates underutilized computing resources from independent data centers, cryptocurrency miners, and excess GPUs from projects like Filecoin and Render. This creates a powerful, accessible, and cost-effective solution for developers and projects.
This fully managed service ensures instant GPU availability, significant cost savings, and enhanced privacy and security, addressing the computing challenges in AI and machine learning fields.
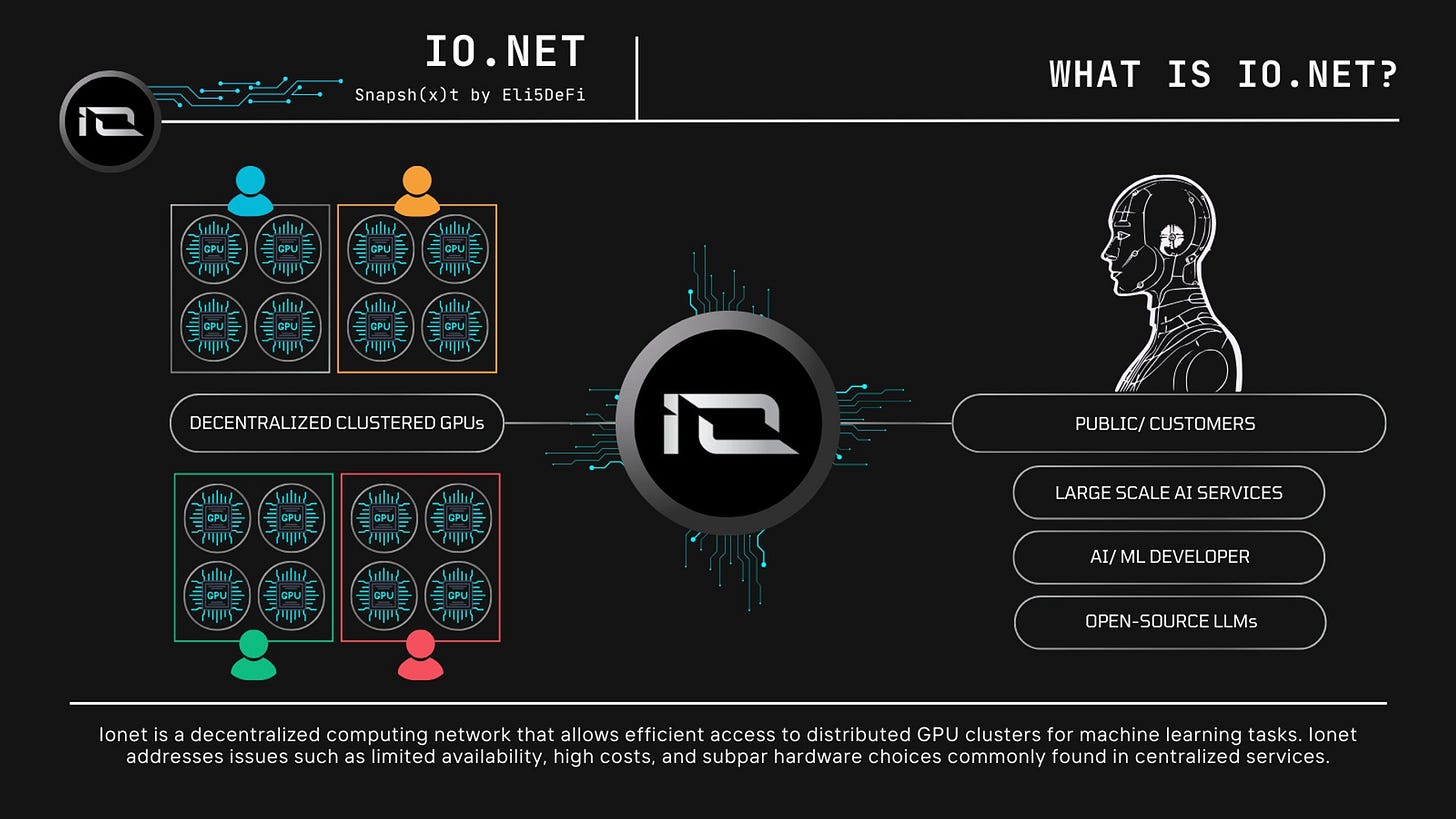
Core Features of IO.net
Decentralized GPU Network
Aggregates global GPU resources, creating a vast pool for AI and ML.
Provides scalable, flexible access to GPUs for various workloads.
Permissionless Access
Allows anyone to join as a Worker or Developer without approval, democratizing high-performance computing access.IO Cloud: Distributed cloud platform for rapid deployment of decentralized ML clusters.
IO-SDK: Proprietary fork of Ray, offering open-source tools for AI model building, used by OpenAI and Uber.
Modular Architecture: Layered design ensures reliability and flexibility with separate UI, security, API, backend, database, message broker, and infra layers.
Working of the Marketplace
Adjusts prices based on job complexity, urgency, and supply, ensuring competitive rates and fair compensation.
Pairs GPU providers with developers based on GPU type, capacity, location, and reputation.
Payments
Supports payments based on $IO. & USDC
Incentivizes $IO usag with 0% fees on txs
Tokenomics of $IO.net
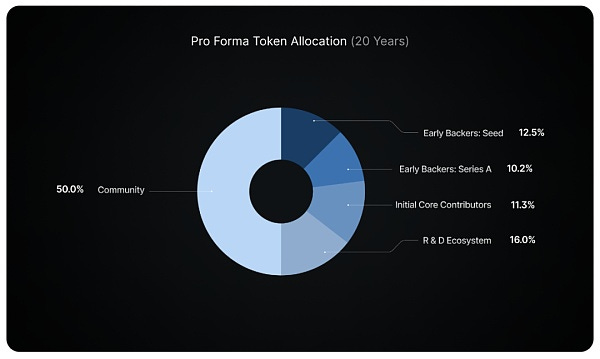
Total supply is of 800 million tokens; 500 million initially distributed, 300 million as rewards over 20 years.
Emission rate decreases 12% annually.
Coin burn mechanism reduces inflation.
Token allocation has been spread across seed investors, series A investors, core contributors, R&D and the major component is allocated to the community (50%)
How does $IO.net toknen accrue value?
Primary currency for computing transactions.
Rewards GPU Renters, Owners, and IO Holders.
Simplifies transactions, promoting demand.
Earns from transaction fees.
Fixed supply, decreasing emissions, and coin burns increase value.
Aethir Cloud
Aethir Cloud is a decentralized platform for high-performance computing, focusing on AI and cloud gaming. It aggregates GPU resources to meet industry demands efficiently.
Core Features and USP
Combines idle GPUs from enterprises, data centers, miners, and retail providers, resulting in higher utilization and competitive pricing.
Scalable infrastructure for demand spikes, high-quality game rendering streamed to low-end devices, targeting underserved regions.
Unified interface that aggregates dispersed computing power for global accessibility.
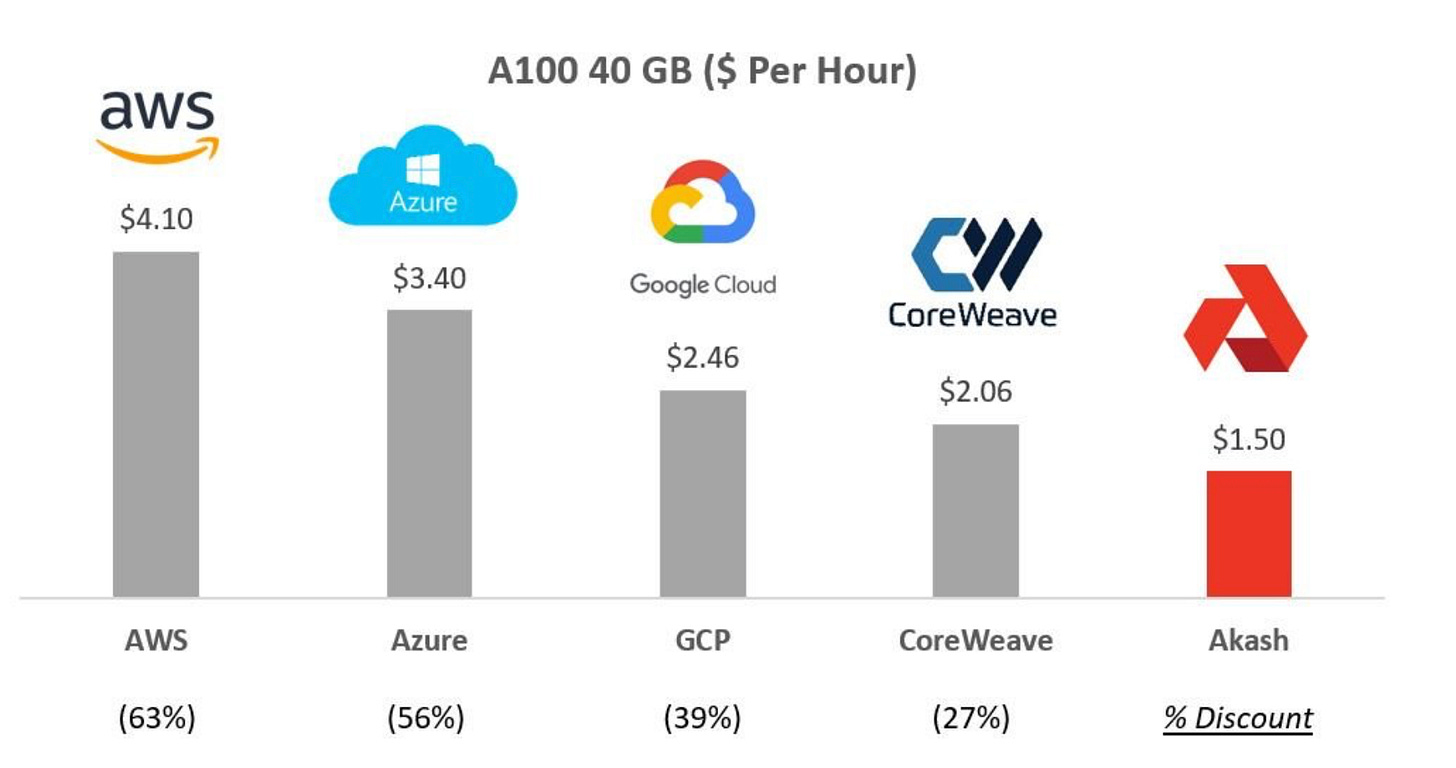
Provides high-end GPUs like the A100 globally at favorable rental rates to enterprise grade users
Recent Traction and Numbers
Partnerships: Deals with major telecoms, gaming publishers, and WellLink, accessing 10 million potential users.
GPU Network: 41,756 connected GPUs, including 3,000 H100 GPUs; A100 rentals at $0.33 per hour
Revenue: $100 million in Q1 2024 from node sales; over $20 million in annual recurring revenue from existing contracts; $1.8 million in service fees.

Core Differentiators
Technical Edge: Offers various network access options, transparent evaluation, and low-latency technologies.
Market Positioning: Competitive pricing, key partnerships, and a strong user base.
Tokenomics of $ATH
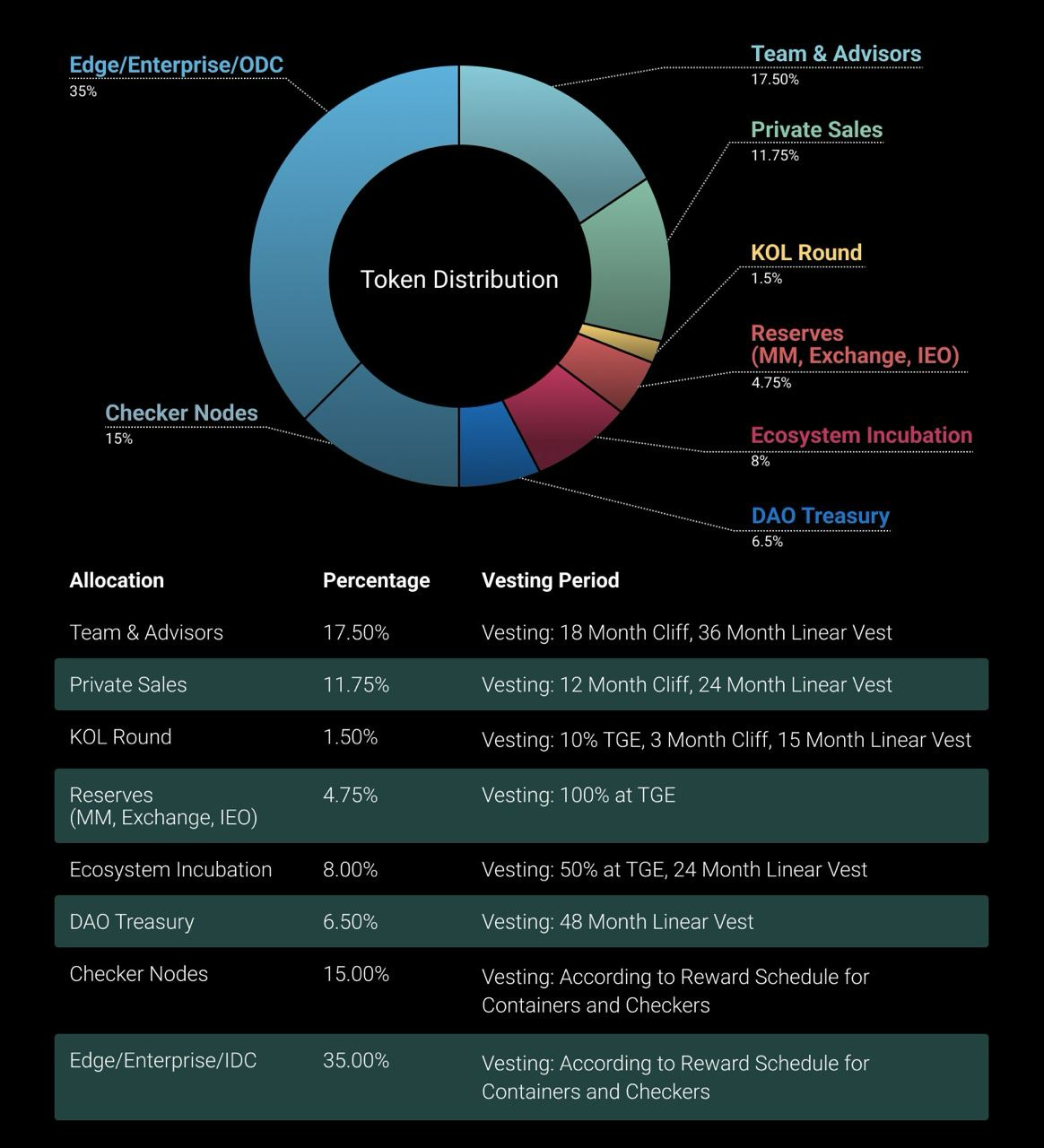
Supply: 42 billion ATH tokens
Detailed yearly emissions aligned with economic strategies
Balanced allocation for short- and long-term stakeholders
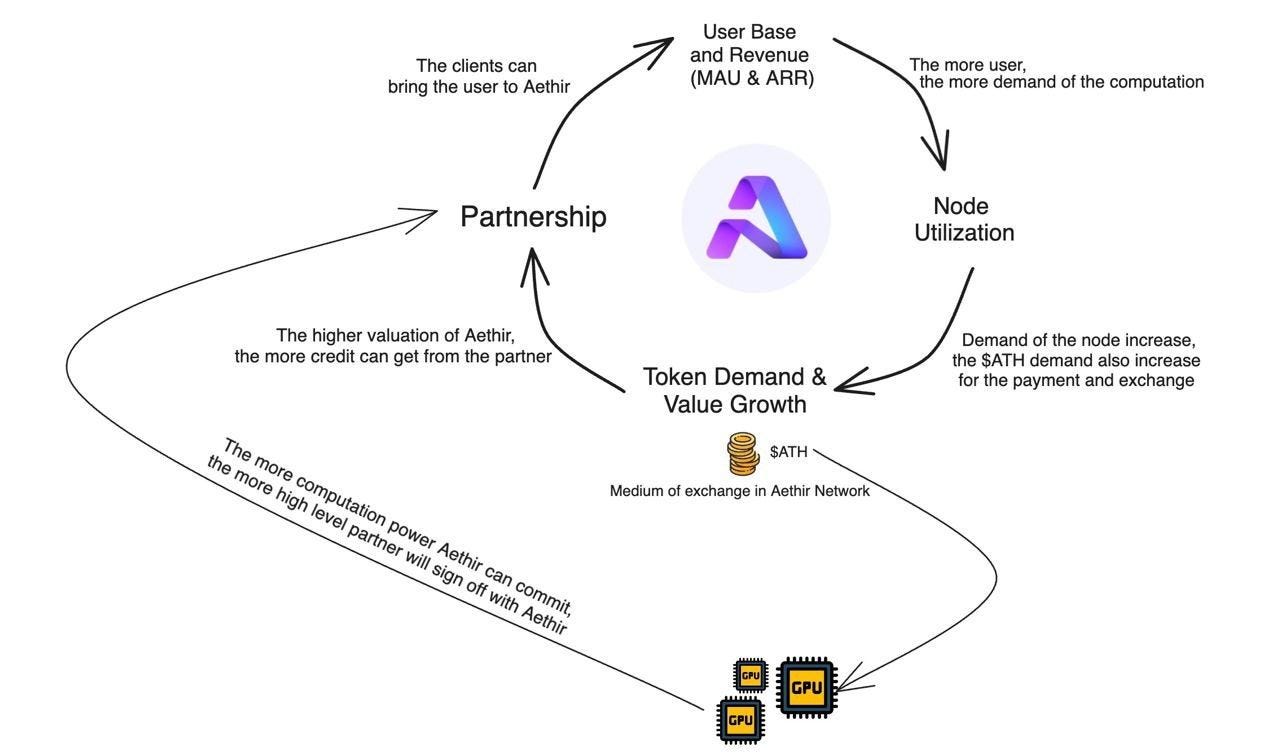
How does the $ATH token accrue value?
ATH token powers transactions, governance, and platform development. Checker Nodes and Containers earn ATH rewards, driving demand.
Token holders can participate in the governance decisions
Controlled emission schedule creates scarcity, possibly also leading to increase in token value over time
High community engagement and checker node license purchases indicate strong demand and growth potential.
Competitive Analysis
To better understand the competitive landscape of the four networks discussed above, please refer to the comprehensive comparison table we have created below.
This aim is to try and provide a clear side-by-side overview of each network's against each other. Check it out here.

Additionally, for a detailed technical comparison, check out the excellent analysis conducted by the impossible finance team.
New Competition and Innovation In Market
New players like NodeAI and GPU.net are entering the decentralized compute space, directly competing with established platforms like Akash and Render.
NodeAI & GPU.net both focuses on ease of accessibility for renting and borrowing GPUs overlapping with Akash and Render. These new projects are trying to bring innovative approaches trying to create a differentiated market for themselves from the already existing top guns.
Projects like Gensyn, and Prime Intellect are working on other unique solutions.
Gensyn is building a global supercluster, promoting efficient model training topped with blockchain incentives.
Prime Intellect democratizes AI development by enabling fair compensation for contributors and secure use of proprietary data.
Prodia Labs is another one that stands out, they’re building the tech for AI-based dynamic image content creation through a singluar API service they’ve created. Some interesting numbers:
Some of their customers do over 1mn generations per day
Pixlr, which comes up as the first recommendation when you google “ai image editor“ - is also powered by Prodia.
It's also worth noting that there is still significant room for collaboration and coopetition in the decentralized compute space.
Many of these projects are building on top of each other's technologies and exploring ways to work together.The overall growth of the ecosystem benefits all players, even if they are competing for certain use cases
Role of Other Crypto x AI Categories in Driving Demand for Compute
The other categories in the Crypto x AI landscape also can contribute demand extensively for the increase in demand of compute resources. Some of them can be:
Training complex models for decentralized applications requires substantial computational power.
Real-time inference in blockchain-integrated AI systems, like DeFi platforms with AI-driven analytics, needs consistent and robust compute resources.
Processing large datasets for AI tasks involves intensive operations like data cleaning and feature engineering.
Reinforcement learning, used in algorithmic trading and autonomous agents, demands significant GPU resources.
Generative AI, such as NFT creation and blockchain-based content generation, also requires powerful compute for both training and inference.
Edge computing for blockchain nodes and IoT devices demands specialized resources for efficient and low-latency operations.
AI agents that automate smart contract management and decentralized decision-making need continuous learning and adaptation, driving compute demand.
Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning (ZKML) enhances privacy-preserving AI in blockchain, requiring optimized compute to generate zero-knowledge proofs.
These diverse applications underscore the critical role of decentralized GPU platforms in providing scalable, efficient AI compute infrastructure, assisting the growth of the larger Crypto x AI ecosystem.
Downsides & faced by decentralised compute networks
Decentralized compute networks offer significant promise but often face notable challenges.
Reliability concerns arise due to the distributed nature of these networks, which introduce potential points of failure and may not match the high uptime and predictable performance of centralised options.
Limited access to the latest hardware, such as Nvidia's H100 and A100 GPUs, can restrict performance, as these are often allocated to major cloud platforms.
Supply and demand imbalances challenge the economic viability of decentralized networks, with many platforms having an oversupply of resources compared to current demand.
Regulatory complexities also pose significant issues, as decentralized compute involves data storage and processing across multiple jurisdictions, complicating compliance.
Building trust and forming strong partnerships with enterprises is another hurdle, as decentralized providers need to demonstrate reliability and scalability.
Poorly designed tokenomics can lead to centralization, undermining the network's decentralized nature. Migration from centralized systems presents performance and technological maturity concerns, making enterprises hesitant to switch.
Security risks remain, as decentralized networks are vulnerable to infiltration by malicious nodes. Robust security measures are crucial to protect against these threats.
While decentralized compute holds great potential, overcoming these challenges is essential for broader adoption and success.
Closing thoughts
Decentralized AI compute networks are transforming AI by utilising the spare computing power.
Major players like Render, Akash, IO.net, and Aethir Cloud are making high-performance computing more accessible and cost-effective. These networks tackle high costs, security concerns, and scalability issues of centralized systems.
Large language models like ChatGPT highlight the need for decentralized compute platforms. Successful projects like IO.net and Aethir Cloud, along with rising investments in AI-related Web3 projects, show strong market potential. The ecosystem is evolving, with decentralized AI compute networks becoming key for AI and Crypto integration.
Though still challenges do remain, such as reliability, hardware access, and regulatory issues. Overcoming these is crucial for wider adoption and trust.
As these networks mature, they are set to play a major role in providing efficient and secure products for the greater good of the technological landscape.
References
Trends in the Dollar Training Cost of Machine Learning Systems by Epoch AI
DePIN x AI: An Overview of Four Decentralized Compute Network by TokenInsight
Disclaimer
The Blockcrunch Podcast (“Blockcrunch”) is an educational resource intended for informational purposes only. Blockcrunch produces a weekly podcast and newsletter that routinely covers projects in Web 3 and may discuss assets that the host or its guests have financial exposure to.
Some Blockcrunch VIP posts are written by contractors to Blockcrunch and posts reflect the contractors’ independent views, not Blockcrunch’s official stance. Blockcrunch requires contractors to disclose their financial exposure to projects they write about but is not able to fully guarantee no such conflicts of interest exist. Blockcrunch itself will not buy or sell assets it covers 72 hours prior to and subsequent to the publication of a piece; however, its directors, employees, contractors and affiliates may buy or sell assets prior to or subsequent to publication of any content and will make disclosures on a best effort basis.
Views held by Blockcrunch’s guests are their own. None of Blockcrunch, its registered entity or any of its affiliated personnel are licensed to provide any type of financial advice, and nothing on Blockcrunch’s podcast, newsletter, website and social media should be construed as financial advice. Blockcrunch also receives compensation from its sponsor; sponsorship messages do not constitute financial advice or endorsement.
For more detailed disclaimers, visit https://blockcrunch.substack.com/about