Exploring the Frontier of Bitcoin Layer 2s: Unlocking BTC's Full Potential
Will Bitcoin L2s be Bitcoin's DeFi summer?
Blockcrunch VIP is a premium research newsletter on the most important crypto projects and trends, prepared by top crypto analysts twice a month. Subscribe to Blockcrunch VIP to receive in-depth project analysis from our research team - all for the price of a coffee ☕ a day.
Bitcoin has had a remarkable journey since its inception in 2009, from its early days as a niche digital currency to the launch of the Bitcoin Spot ETF in 2023 which marked a significant milestone in turning Bitcoin into a mainstream asset class. Now institutional investors are able to gain exposure to the world's largest cryptocurrency with ease and BiTC net inflows have already surpassed $1B as of March 15, 2024.
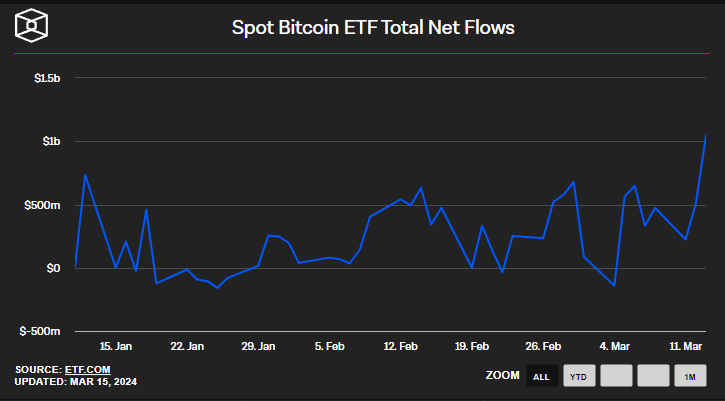
In fact, ever since the BTC ETF was created, the net BTC inflows have been higher than the amount of BTC mined. For example, in the first week of March, the BTC ETF inflows equaled 33,000 Bitcoin, while Bitcoin miners produced 6300 BTC, showing that demand is outpacing supply significantly.

Additionally, BTC reserves in exchanges continue to dwindle, likely sitting on-chain in self-custodial wallets. The drop in BTC on exchanges has often been viewed as a bullish signal.

To top things off, the upcoming halving event in 2024 is happening in April 20, 2024, or roughly 30 days later as of this writing. This will halve the rate at which new bitcoins are mined, which is likely to further exacerbate the supply-demand imbalance, driving prices even higher.
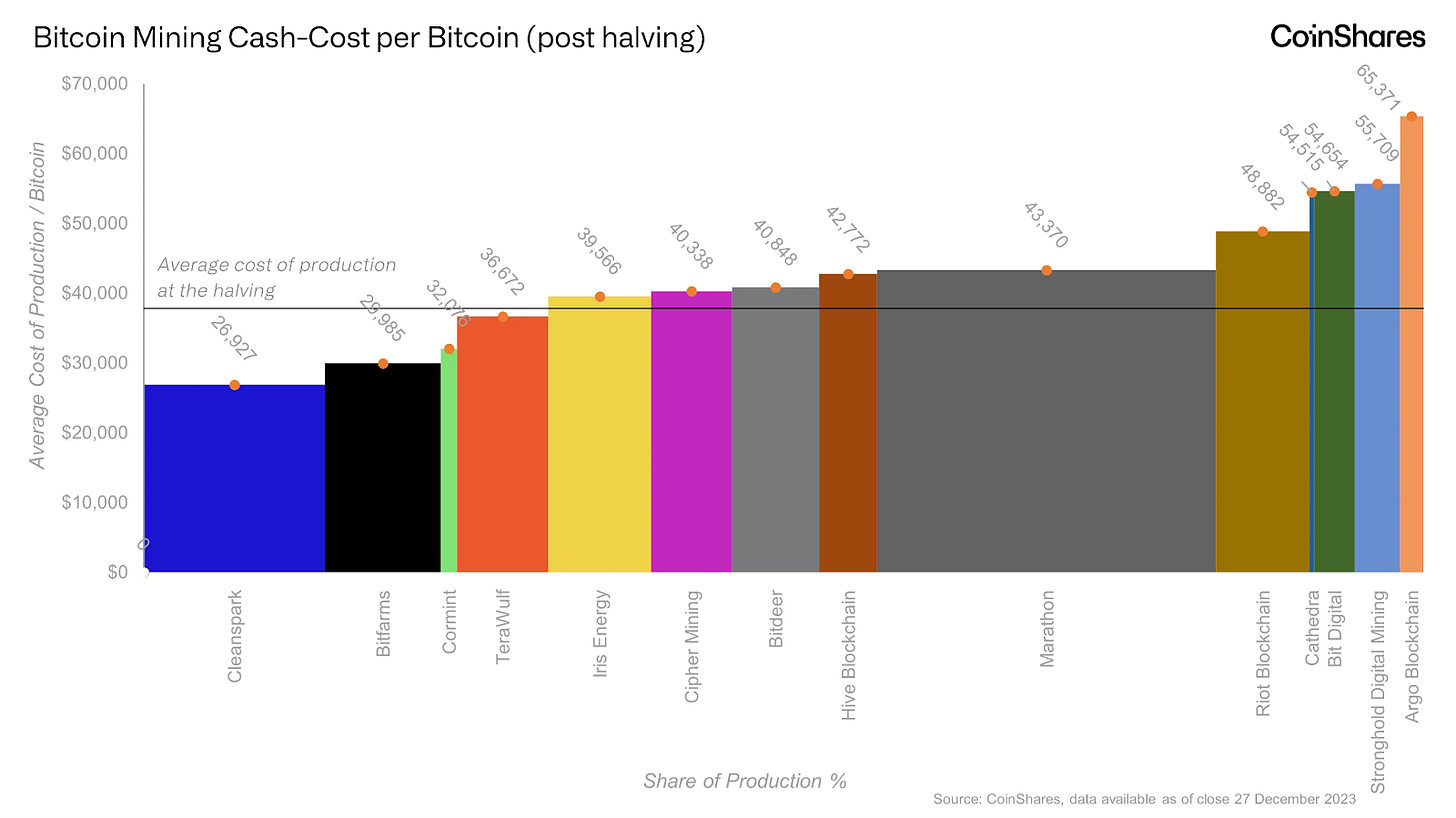
For miners, the halving also means that their cost per bitcoin will increase. The cost of BTC production has often acted as a lower boundary of Bitcoin’s price range, or aka price floor, as miners are not able to sustainably sell below this level. Bitcoin's current production cost is estimated to be about $18,000 to $21,000. According to CoinShares research, the average cost of production is estimated to be around $38k after the halving, rising bitcoin’s floor price.
All these factors have no doubt helped Bitcoin’s price finally achieve an all time high after roughly 850 days, now hitting over $1.3 trillion in market cap. With BTC outperforming most other cryptocurrencies, this has led to BTC continuing to dominate mindshare.
However, despite its meteoric rise, Bitcoin's underlying technology has faced criticism for its limited programmability and scalability. Furthermore, with BTC ETFs growing market share rapidly, there are concerns of BTC centralization, turning Bitcoin into a controlled asset within the traditional financial system.
Could this be Bitcoin’s DeFi summer, awakening this sleeping giant and turn into something more productive while furthering its decentralization?
This is where Bitcoin Layer 2 (L2) solutions come into play. There are now numerous Bitcoin L2 protocols aiming to improve upon Bitcoin's capabilities by introducing additional features and functionalities without compromising the core principles of decentralization and security.
In the following sections, we will explain what a Bitcoin L2 is, the problems it is solving, comparing the different Bitcoin L2s, and exploring possible future use cases and risks that Bitcoin L2 faces.
Understanding Bitcoin L2s
What are Bitcoin L2s?
According to Bitcoin Magazine, they define Bitcoin L2s as:
Use Bitcoin as a native asset
Use Bitcoin as a settlement mechanism to enforce transactions, allowing users to return control of assets to Layer 1
Demonstrate functional dependence on Bitcoin, meaning the system cannot continue operating if the Bitcoin network fails
However, this definition would disqualify most existing Bitcoin L2s. The minimum requirement for a Bitcoin L2 is to derive its security from Bitcoin, the most secure blockchain due to its extensive proof-of-work consensus mechanism.
In this context, 'security' refers to mechanisms that validate the operations and transactions of the L2, potentially by verifying computations through proofs, similar to how Ethereum secures its rollups. However, Bitcoin's architecture was not originally designed to support complex smart contract executions or direct verification of such proofs.
Bitcoin L2 solutions often rely on different mechanisms to ensure security. Typically, they anchor their state and transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain, leveraging its security indirectly, often through inscriptions. Unfortunately, inscriptions have limited throughput (approximately 1.1 KB/s), posing a scalability challenge.
To address this, these L2 solutions record final states or commitments on the Bitcoin blockchain, ensuring tamper-evidence and benefiting from Bitcoin's security properties, even if Bitcoin itself does not directly validate the individual operations of the L2.
While Bitcoin does not verify operations of an L2 like Ethereum does with its rollups, anchoring an L2's state and transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain and using Bitcoin as a DA layer that is monitored by third parties to validate the L2's state, is currently regarded as a way to secure Bitcoin L2 by associating them with Bitcoin's security and immutable consensus.
In the future, proposals to introduce new opcodes (operation codes) to Bitcoin could allow it to validate zero-knowledge proofs submitted by zk-rollups. Additionally, protocols like BitVM is aiming to enable fraud proof validation on Bitcoin without requiring changes to the base layer protocol, revolutionizing the way Bitcoin L2s solutions interact with the Bitcoin mainnet.
Now that you understand what makes a Bitcoin L2 and the differences from Ethereum L2s, let's explore the different types of Bitcoin L2s.
Types of Bitcoin L2s
Bitcoin L2s can come in various forms, each with its own set of tradeoffs and design choices. The main types include state channels, sidechains, and rollups.
State channels: The simplest of L2s, state channels enable instant and nearly free transactions by establishing off-chain payment channels between parties. The Lightning Network is the most popular example of a state channel, allowing users to transact privately without broadcasting each transaction to the Bitcoin mainnet.
Sidechains: Unlike state channels, sidechains are independent blockchains with their own consensus mechanism and validator set, and transactions are settled and finalized without relying on Bitcoin. While sidechains primarily derive security from their own tokens, some projects like Stacks aim to inherit security from Bitcoin through mechanisms like proof-of-transfer. Rootstock and Stacks V1 are popular examples of sidechains that are currently live.
Rollups: Rollups are a more recent innovation that offer the scalability benefits of sidechains while deriving more security from the Bitcoin base layer. They bundle multiple transactions into a single on-chain transaction on the Bitcoin network for consensus and finality. Rollups can be categorized into two main variants:
1. Optimistic Rollups: These rollups assume transactions are valid by default and only rely on fraud proofs to challenge invalid transactions. They offer improved scalability but have longer withdrawal times due to the challenge period.
2. ZK Rollups (Validity Rollups): These rollups use zero-knowledge proofs to validate the correctness of transactions off-chain, providing faster finality and shorter withdrawal times. However, they are more computationally intensive and harder to develop compared to Optimistic Rollups.
Sovereign Rollups: A distinct type of rollup that operates independently of the Bitcoin mainnet, using it primarily for data availability purposes. They differ from optimistic and ZK rollups in their settlement model and trust assumptions. Citrea is an example of a sovereign rollup currently in development. Rollkit, a development framework developed by Celestia, allows a chain to become a sovereign rollup on Bitcoin easily.
Here’s a comparison table between the different types of Bitcoin L2s that I made.
Each type of L2 solution comes with its own set of tradeoffs and design choices. State channels offer high scalability and security but require participants to be online and have limited functionality. Sidechains provide flexibility and customization but may have higher trust assumptions. Rollups strike a balance between scalability and security, with Optimistic Rollups being easier to implement but requiring longer withdrawal times, while ZK Rollups offer faster finality but are more complex to develop.
As the Bitcoin L2 ecosystem continues to evolve, we can expect to see further innovations and hybrid approaches that aim to optimize the tradeoffs between scalability, security, and functionality.
Why do we need Bitcoin L2s?
As Bitcoin continues to gain mainstream adoption, the limitations of its base layer have become increasingly apparent. While Bitcoin excels at providing a secure, decentralized, and censorship-resistant store of value, it faces challenges in terms of scalability, programmability, privacy, and decentralization.
This is where Bitcoin Layer 2 (L2) solutions come into play, aiming to address these limitations and unlock the full potential of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Here are some of
1. Scalability: Bitcoin's base layer is inherently limited in terms of transaction throughput, with a theoretical maximum of around 7 transactions per second (TPS). As more users adopt Bitcoin, this limitation becomes a bottleneck, leading to slower confirmation times and higher transaction fees. L2 solutions aim to alleviate this issue by moving a significant portion of transactions off-chain, allowing for faster and cheaper transfers while still leveraging the security of the Bitcoin mainnet.
2. Programmability: Bitcoin L2s introduce more flexible and expressive programming environments, enabling developers to build a wide range of applications on top of Bitcoin, from decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and beyond.
3. Privacy: L2 solutions can enhance privacy by keeping transactions off-chain and using techniques like zero-knowledge proofs to obfuscate transaction details. State channels, such as the Lightning Network, enable private, off-chain transactions between parties, while zkRollups can bundle multiple transactions together, making it harder to trace individual transfers.
4. Decentralization: The recent approval of a Bitcoin ETF has raised concerns about the potential for increased centralization. L2 solutions can help mitigate this risk by providing individuals with more options for non-custodial ownership and participation in the Bitcoin ecosystem. By enabling a wider range of use cases and yield opportunities, L2s can incentivize users to hold and transact with Bitcoin directly, rather than relying on centralized intermediaries.
5. Yield opportunities:
Bitcoin L2s will also offer new avenues for earning yield on BTC through DeFi activities such as liquidity provision in DEXs, lending, borrowing, staking BTC to provide security, etc. This potentially transforms BTC from a mere store of value to a dynamic asset within the broader Bitcoin economy. This development could significantly bolster Bitcoin's utility and value as a decentralized financial asset, supporting its long-term significance in the digital economy.
6. Trust-minimized Bridging

The most popular form of tokenized BTC that can be used in DeFi right now is wBTC which has a market cap of around $10 billion, followed by Huobi BTC at $128 million. Both wBTC and HBTC are regarded as centralized bridging solutions. Development into Bitcoin L2s also means development into safer trust-minimized BTC bridges to facilitate transfers from the main chain to L2s, which could be safer compared to centralized and custodial solutions, helping to maintain Bitcoin's core values of security and decentralization.
Bitcoin L2 Impact on Miner Revenue:
The upcoming Bitcoin halving in 2024 will half the block reward for miners, which is a proxy to Bitcoin’s security budget. Miners will look towards other fees to sustain profitability.
Bitcoin Layer 2 (L2) solutions offer a pathway to enhance these fee revenues by creating a higher demand for block space. This, in turn, drives up transaction fees, benefiting miners. As L2 adoption increases, the bundling of numerous off-chain transactions into single on-chain settlements will further intensify the competition for block space, thereby raising transaction fees and offering miners a valuable source of income post-halving.
The Ordinals Protocol has generated over $400m in fees to date but the volume has tapered off as ordinals were largely driven by unsustainable hype due to the lack of utility.
Bitcoin L2s on the other hand is expected to offer real value and utility to users, allowing miners to generate more sustainable revenue. This not only secures a steady fee income for miners but also underpins the growth and development of L2 solutions, creating a virtuous cycle that benefits the entire Bitcoin ecosystem.
Bitcoin L2 Landscape
Now that we have a better understanding of Bitcoin L2s, let’s explore existing Bitcoin L2 solutions. Here is a comparison table of the different Bitcoin L2s that we will be exploring:
Stacks
Starting with arguably the most successful Bitcoin L2 at the moment in terms of market cap, ecosystem, and community, Stacks pioneered the Bitcoin L2 movement by leveraging Bitcoin as a settlement layer to bring smart contract functionality and decentralized applications (dApps) to the Bitcoin network.
Stacks was developed by Blockstack PBC, a company founded in 2013 by computer scientists Muneeb Ali and Ryan Shea from Princeton University and raised over $75 million from notable investors such as Union Square Ventures, Y Combinator, Lux Capital, Rising Tide, Recruit Holdings, and Hashkey Capital. Some of the early investors and advisors include Naval Ravikant, Balaji Srinivasan, and Anthony Pompliano. With a strong technical team and backing from prominent investors in the blockchain and cryptocurrency space, Stacks has positioned itself as a leading contender in the race to bring decentralized applications and financial services to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
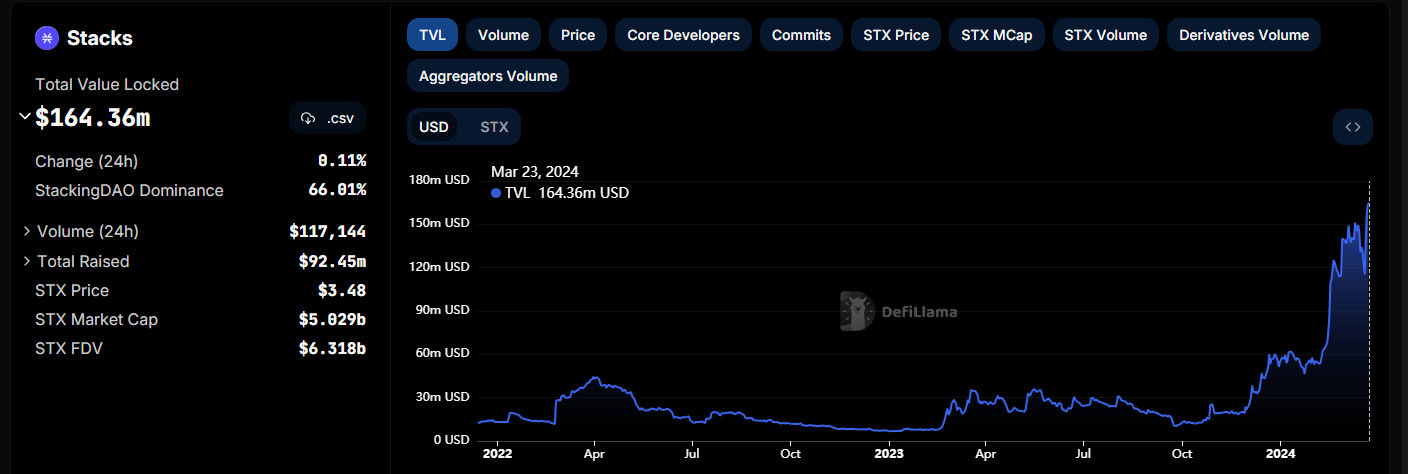
Stacks experienced significant growth in 2024, and according to Messari, they generated over $600k in revenue last year. The STX token has also outperformed Bitcoin by over 50% and as of 23 March 2024, it’s market cap has exceeded $5 billion.

Stack’s key features include:
Proof-of-Transfer (PoX): Stacks utilizes a unique consensus mechanism called "proof-of-transfer," where miners submit bids in BTC on the Bitcoin blockchain to earn the chance to create the next block and are rewarded with the native STX token. This is also known as “Stacking”.
Full Bitcoin State Knowledge: Stacks has knowledge of the full Bitcoin state, thanks to its Proof-of-Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism and Clarity programming language, enabling it to read from Bitcoin at any time.
Nakamoto Release Upgrade: This is a major upgrade enabling block times to move from the current 10 minutes to seconds, anchor transactions to Bitcoin for 100% Bitcoin finality, reduce MEV, and set the stage for the upcoming sBTC release.
sBTC: Aiming to be the first decentralized, non-custodial Bitcoin peg that is operated by a dynamic set of crypto-incentivized "Stackers," enabling users to leverage Bitcoin's security and decentralization for various DeFi activities and also allow smart contracts to write back to the Bitcoin blockchain. It entered alpha testing in Q2 2023 and a closed incentivized testnet in Q4 2023 with mainnet in July 2024.
What puts Stacks in a different league from other Bitcoin L2s is its robust ecosystem, which it has had several years of headstart on. The Stacks ecosystem expanded quickly and successfully attracted new users through incentive programs. Stacks' TVL is at an all-time high of $164 million as of 23 March 2024, increasing by about 5 times since last year, driven by the launch of new protocols and bridges.
Let’s take a quick look at some of Stack’s ecosystem dApps:
ALEX Labs: ALEX is the first one-stop shop for decentralized financial services on Bitcoin, offering a comprehensive suite of DeFi services, including a token launchpad, an advanced DEX combining automated market making and order books, lending and borrowing services for Bitcoin, and leverage products such as margin swaps and yield farming. It was developed by a team of veteran Wall Street quants and finance experts, including CEO Chiente Hsu, Ph.D., formerly the Global Head of Alpha Strategies at Credit Suisse, and co-founder Rachel Yu, M.S., an alumnus of Goldman Sachs and JP Morgan Asia.
Arkadiko: Arkadiko's stablecoin, USDA, is collateralized by STX tokens locked in smart contracts, ensuring transparency and decentralization. The platform also offers a DEX for trading USDA and other Stacks-based tokens, fostering liquidity and enabling users to seamlessly exchange assets within the Stacks ecosystem.
Velar Perp DEX: Velar is a perpetual derivative exchange built on the Stacks blockchain. Velar has garnered significant support from prominent investors, having raised $3.5 million in a seed funding round led by Artemis Capital, Transform Capital, Bitcoin Startup Lab, and Rocinante Research, with participation from various other notable venture capital firms and individuals in the blockchain space. One of Velar's unique features is its IDO launchpad, allowing tokens to be launched on Stacks. Velar will also feature a Uniswap V2 style DEX, offering users a simple and permissionless trading experience.
Gamma: A pioneering NFT marketplace built on the Stacks blockchain, leveraging Bitcoin's security and NFT capabilities introduced by Ordinals.
StackingDAO: A liquid staking protocol enabling users to stake their STX tokens in return for an STX LSD which continues to accrue STX staking rewards while being liquid.
STX20: An innovative inscription protocol, inspired by the Bitcoin Ordinals project. It allows users to inscribe arbitrary data, including NFTs, onto the Stacks blockchain, leveraging the security and immutability of Bitcoin while benefiting from the smart contract capabilities of Stacks.
Zest: A lending protocol enabling users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies in a decentralized and trustless manner.
With major upgrades like Nakamoto and the introduction of innovative protocols like sBTC on the horizon, Stacks continues to evolve and position itself as a leading Bitcoin Layer 2 solution. It is poised to drive the growth of Bitcoin-based DeFi and provide users with trust-minimized access to Bitcoin liquidity, further solidifying its position as a prime contender in the Bitcoin Layer 2 landscape.
However, Stacks' lack of Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility may hinder its path to mass adoption, as upcoming EVM-compatible Bitcoin L2 solutions could potentially pose a threat by leveraging the existing Ethereum ecosystem and tooling, potentially attracting more developers and users to their platforms. Let’s explore some of those starting with Merlin Chain.
Merlin Chain
Merlin Chain is a ZK Bitcoin Rollup that can support multiple types of native Bitcoin assets while being EVM compatible.
It offers a comprehensive scaling solution that integrates a ZK-rollup network, a decentralized oracle network, and on-chain Bitcoin fraud proof modules. This multi-faceted approach promises to address some of the key challenges faced by Bitcoin, including scalability, privacy, and programmability.
The protocol was developed by Bitmap Tech, the team behind the wildly successful Ordinals project BRC-420 "Blue Boxes,". They have garnered significant attention and funding from prominent investors like OKX Ventures, ABCDE, Foresight Ventures, and Arkstream Capital.
Merlin Chains’s key features include:
Polygon CDK Validium Architecture: Merlin Chain leverages the Polygon CDK Validium architecture, which combines Polygon's zkEVM with a decentralized oracle (DAC) to inherit Bitcoin's robust security through a multi-signature mechanism compatible with Bitcoin's Taproot upgrade.
ZK-Rollup Component: Merlin Chain features a ZK-rollup component that bundles and validates transactions off-chain using zero-knowledge proofs, reducing the load on the Bitcoin mainnet while maintaining strong security guarantees.
Scalability and Throughput Improvements: By compressing transaction data into succinct validity proofs posted on-chain, Merlin Chain aims to achieve substantial throughput improvements over the base layer without compromising decentralization.
On-Chain Bitcoin Fraud Proof Modules: Merlin Chain incorporates on-chain Bitcoin fraud proof modules, leveraging concepts like BitVM to enable trustless and decentralized verification of Layer 2 transactions directly on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Unique Account Abstraction Model: Merlin Chain adopts Particle Network's BTC Connect, a unique account abstraction model that allows Ethereum's externally owned accounts (EOAs) to be calculated using Bitcoin's public keys, enabling Bitcoin native wallets like Xverse to interact with EVM smart contracts on Merlin Chain.
Following Merlin’s mainnet launch, the team plans to host a series of staking events and distribute its governance token MERL through a "fair launch" process, rewarding active users and builders who contribute to the ecosystem's growth.
In summary, Merlin Chain stands out as a unique Layer 2 solution that bridges the Bitcoin and Ethereum ecosystems, inheriting the security of Bitcoin while leveraging Ethereum's vibrant dApp ecosystem, and fostering innovation through novel protocols and a strong focus on security and ecosystem development.
BOB
BOB, short for "Build on Bitcoin," is an EVM-compatible Bitcoin L2 designed as a Bitcoin co-processor. It was developed by the Interlay ecosystem, which emerged from the Polkadot and Cosmos projects.
At its core, BOB is looking to become a comprehensive stack for building decentralized applications (dApps) on top of Bitcoin, using the Bitcoin L1 for settlement, custody, and storage, while bridging the gap between the Bitcoin and Ethereum ecosystems.
BOB's key features include:
Bitcoin Security: BOB allows inheriting Bitcoin's Proof-of-Work (PoW) security, and will start off utilizing an optimistic rollup design with the long-term goal transitioning to a more trustless approach by settling transactions directly on Bitcoin via zero-knowledge proofs.
Support for the Bitcoin Stack: BOB supports the existing Bitcoin tech stack, including Ordinals, Lightning, and Nostr, powered by cross-chain light clients, a universal Bitcoin smart contract SDK, a Rust zkVM for supporting Bitcoin’s Rust libraries, and trustless Bitcoin bridges for secure asset transfers.
EVM Compatibility: BOB smart contracts are powered by the EVM, ensuring full compatibility with best-in-class infrastructure and tooling from the Ethereum ecosystem.
ETH Rollup Support: BOB supports rolling up to Ethereum as an OP stack rollup with a native Ethereum bridge, unlocking Bitcoin use cases for web3 power users, including access to DeFi liquidity and easy on/off-ramps from major exchanges and institutional platforms.
Currently in public testnet, BOB is actively working towards its mainnet launch, during which it will showcase its full capabilities and potential. With its strong focus on experimentation, real-world impact, and freedom of choice for builders, BOB is positioning itself as a pioneering platform for the Bitcoin building renaissance.
Citrea
Citrea is revolutionizing the Bitcoin ecosystem by introducing a first-of-its-kind rollup that leverages zero-knowledge technology to unlock unprecedented scalability and security on Bitcoin, all without altering its foundational consensus rules.
Backed by an impressive lineup of investors, including Delphi Ventures, Eric Wall—co-founder of the Taproot Wizards NFT project—and Anurag Arjun, co-founder of the data availability blockchain Avail, Citrea stands at the forefront of innovation, promising to drive the next wave of growth and adoption in the Bitcoin network.
Citrea’s key features include:
Type 2 zkEVM: Citrea leverages zero-knowledge proofs to process zkEVM transaction batches, submitting them to Bitcoin in an inscription-like format. This approach ensures batch validity verification while maintaining the network's integrity.
BTC as Native Token: Citrea uses $BTC as its native token, designated as $cBTC within the Citrea ecosystem to distinguish it and streamline the user experience for on/off-ramp transactions.
Proofs Inscribed in Bitcoin: Utilizing BitVM, Citrea inscribes its zero-knowledge proofs directly onto the Bitcoin blockchain. These proofs, which detail the state differences resulting from transaction batches, are optimistically verified and accessible to anyone running a Bitcoin node.
Support for Light Nodes: Citrea employs STARK-based recursive zero-knowledge proof systems to facilitate easy verification by light nodes. This reduces the full dataset to a small proof that integrates seamlessly with Bitcoin, enabling trustless verification and state access even for Bitcoin Light Nodes (SPV).
Universal Trust-Minimized Two-Way Peg: The protocol introduces a novel two-way peg mechanism verified on Bitcoin through BitVM. This feature uses Taproot to secure pegged BTC in a contract on the Bitcoin network, with withdrawals contingent on valid ZK proofs, ensuring a high degree of security and trust minimization.
These features collectively position Citrea as a significant innovation within the Bitcoin L2 space, promising enhanced scalability, security, and user engagement.
B^2
B^2 (Bsquared) is an EVM-compatible Bitcoin Layer 2 that uses ZK proofs. They are backed by investors like Polychain Capital, Electric Capital, and Sovereign Capital.
Unlike other BTC L2s like Merlin Chain and BOB, which aim to bridge the Bitcoin and Ethereum ecosystems, B^2 takes a more practical approach, leveraging novel techniques like "proofs of proof of work" (PoPoW) to inherit Bitcoin's security while enabling high throughput and arbitrary smart contract execution.
Key features of B^2 Network:
Zero-Knowledge Proof Verification: It was the first Bitcoin rollup to use ZKPs to aggregate transactions into batches and submits succinct proofs to Bitcoin, maintaining transaction privacy while enhancing throughput.
Integration with Portal for Cross-Chain Swaps: Through a partnership with Portal, B^2 Network enables trust-minimized, Layer 2 cross-chain swaps without the need for bridges, custody, or wrapping, expanding the liquidity and usability of its tokens.
B^2 Buzz: A staking event launched by B^2 Network that has attracted over $570 million of TVL where users can deposit Bitcoin, Ethereum, BNB Chain, and Polygon to receive "Parts" used to assemble "Mining Rigs" that mines B^2 Network's native tokens.
B^2 Network’s innovative B^2 Buzz staking event positions them as a prominent player in the EVM-compatible Bitcoin L2 ecosystem, leveraging innovative incentive mechanisms to have a headstart compared to others in terms of liquidity and ecosystem growth.
Now that we’ve explored some of the Bitcoin L2s, let’s attempt to project what the valuation of this category when compared with Ethereum.
Bitcoin L2 Valuation Projections
Disclaimer: The valuations below are purely hypothetical and based on assumptions, and are not an indication of our view on valuations.
Bitcoin L2s are somewhat late to the L2 movement, however, this presents a possible catch-up trade opportunity. As Bitcoin L2 allows for DeFi to flourish while still being secured by Bitcoin, and seen as safe due to the ETF approval, it is likely that more capital will move into protocols building on Bitcoin, such as Bitcoin L2s.
Using data from DefiLlama’s, the current market cap of BTC is around $1.25 trillion with a combined L1 and L2 (including Bitcoin sidechains) TVL of $1.1 billion, while Ethereum’s market cap is $400 billion with a combined L1 and L2 TVL of $65 billion. This means that BTC’s TVL is over 50 times less than Ethereum, and when when comparing the L1+L2 TVL/MCAP of both networks, Bitcoin is about 180x less than Ethereum, which is a huge discrepancy that could be viewed as an opportunity by investors if they believe that TVL will flow into Bitcoin L2s, which is often correlated to market cap growth.

BTC Restaking
We can’t talk about Bitcoin L2s without talking about BTC Restaking. This innovative concept allows users to stake their Bitcoin (BTC) on one platform which then restakes the staked BTC on other platforms to secure it in exchange for certain rewards, increasing the yield generated to BTC. Several projects, such as Lorenzo Protocol, Babylon, and Bouncebit Protocol, are at the forefront of this emerging trend.
Babylon
Babylon protocol pioneered the concept of Bitcoin staking and Bitcoin shared security. It aims to extend Bitcoin's security to enhance Proof of Stake (PoS) systems. It allows Bitcoin holders to leverage their assets to secure PoS chains while earning yields on their staked Bitcoins.
Babylon's protocol eliminates the need for third-party custody, bridging, or wrapping of assets, offering a seamless and secure method for Bitcoin staking directly on PoS chains, without compromising on security.
By allowing the staking of Bitcoin, Babylon significantly increases the capital securing PoS chains, providing heightened security without the high inflation rates typically required to attract staking capital, offering a more sustainable model for long-term growth and stability.
With its Bitcoin timestamping feature, Babylon also supports rapid unbonding of stakes, maximizing liquidity for Bitcoin holders and addressing lengthy unbonding periods, enabling more efficient capital utility.
Designed as a modular plug-in, Babylon's staking protocol can be seamlessly integrated with various PoS consensus algorithms, fostering a more interconnected and secure blockchain ecosystem.
Babylon also shares similarities with Eigen Layer in the sense that they are both using a major cryptocurrency as a collateral to provide shared security for PoS networks in exchange for yield.
The recent launch of Babylon's Bitcoin staking testnet marks a significant milestone, allowing validators to experiment with BTC staking and timestamping in a permissionless environment, paving the way for the full-scale launch of the protocol.
Lorenzo
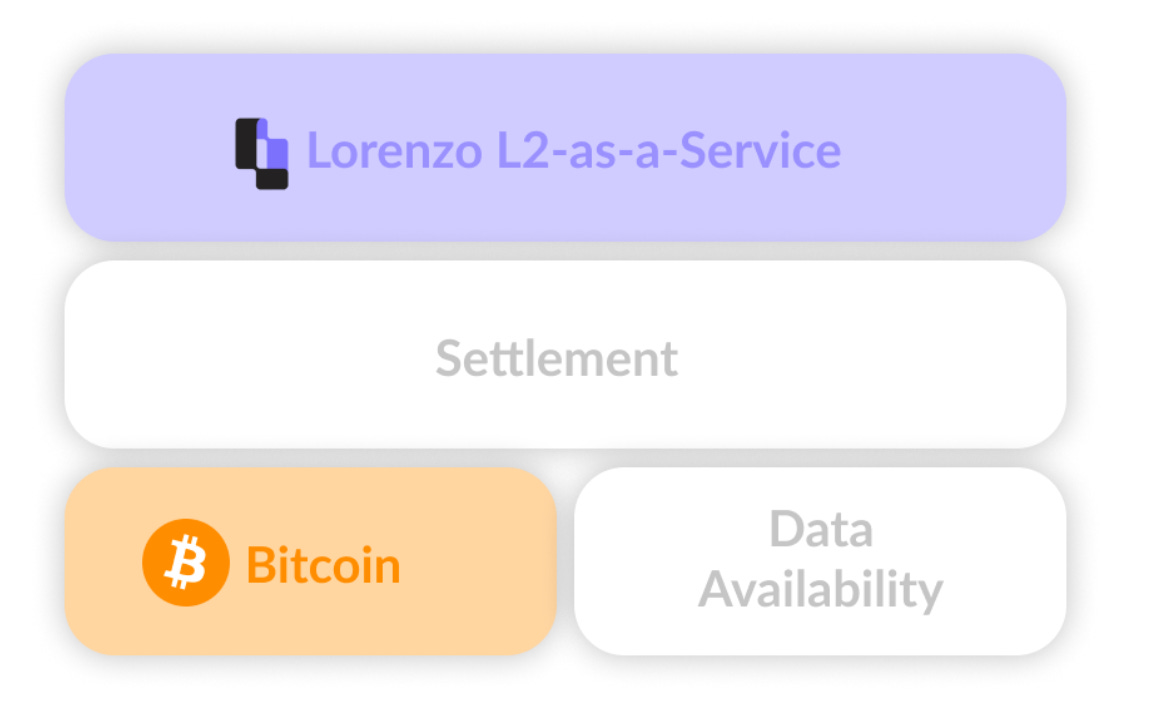
Lorenzo Protocol introduces liquid staking and Layer 2-as-a-Service (L2aaS) to the Bitcoin ecosystem. Their liquid staking solution allows users to stake BTC while maintaining the ability to trade or use their assets, providing greater flexibility compared to traditional staking.
Lorenzo Protocol's BTC liquid staking works by issuing an LBTC token to users when they stake their BTC. The LBTC token represents the staked BTC and can be used across various DeFi applications, including yield farming and lending protocols. This approach enables users to maximize their returns by leveraging their staked BTC across multiple platforms.
The Lorenzo Protocol also offers a range of tools and services for developers to build and deploy Layer 2 solutions on Bitcoin, further enhancing the ecosystem's scalability and efficiency.
Bouncebit

BounceBit presents a paradigm shift in the Bitcoin Layer 2 landscape, drifting away from the traditional Layer 2 approach and towards a standalone Proof of Stake (PoS) Layer 1 ecosystem. At its core, BounceBit introduces an asset-driven philosophy, emphasizing the versatility of BTC and its active role in network validation.
BounceBit distinguishes itself as a standalone PoS Layer 1 ecosystem, requiring validators to stake both native BounceBit tokens and BTC. This dual-token security system not only strengthens the network but also enhances the intrinsic value of BTC by enabling its active participation in network validation.
BounceBit integrates a transparent centralized finance (CeFi) model, utilizing Mainnet Digital's custody services complemented by Ceffu's MirrorX technology. This allows Bitcoin to maintain its on-chain presence while engaging in trading activities on centralized exchanges (CEX), with outcomes reconciled on-chain and a T+1 settlement cycle, ensuring liquidity and transparency.
Recognizing the inherent conservatism of Bitcoin holders, BounceBit implements an initiative aimed at activating the most liquid and actively used BTC such as WBTC from Ethereum and BTCB from BSC, enabling their entry into productive activities and the accrual of on-chain yields without direct interactions with the Bitcoin main chain.
BBTC, a wrapped Bitcoin on BounceBit, offers yield from DeFi opportunities, node staking and PoS mining, and strategic asset management including CeFi funding rate arbitrage facilitated by regulated custodial services. The funding rate strategy sounds similar to Ethena Finance but with a BTC LSD instead of a stablecoin.
BounceBit's vision is to reinforce the integrity and trust inherent in CeFi while establishing a new foundational moment for Bitcoin, akin to Ethereum's pivotal shift with Lido. By enhancing transparency and providing the right incentives, BounceBit aims to solidify trust in CeFi practices and mobilize the active Bitcoin ecosystem.
Challenges and Drawbacks
While Bitcoin Layer 2 (L2) solutions offer numerous benefits and opportunities, they also come with their own set of challenges and drawbacks that must be carefully considered and addressed.
1. Complexity and Potential User Experience Issues:
L2 solutions introduce an additional layer of complexity to the Bitcoin ecosystem, which can impact user experience and adoption. Users may find it challenging to navigate between the base layer and various L2 solutions, each with its own set of rules, interfaces, and requirements. This complexity can create barriers to entry for less technically savvy users and hinder wider adoption.
Furthermore, the user experience on L2s may create more complexity as a user may need to manage multiple wallets, perform additional steps to move funds between layers, or deal with longer confirmation times for certain types of transactions. Addressing these usability challenges is crucial for the adoption of the L2s.
2. Centralization Risks and Trust Assumptions:
Some L2 solutions may introduce centralization risks and require users to place trust in certain entities or mechanisms. For example, sidechains often rely on a federation of validators or a trusted bridge to facilitate the transfer of assets between the base layer and the sidechain. This reliance on intermediaries can create single points of failure and undermine the decentralization ethos of Bitcoin.
Similarly, optimistic rollups rely on a challenge period during which users can dispute fraudulent transactions. If the majority of users or the entities responsible for submitting fraud proofs are compromised or collude, the security of the rollup could be jeopardized. Developers must carefully design L2 solutions to minimize trust assumptions and ensure that the benefits of decentralization are preserved.
3. Interoperability and Composability Concerns:
The proliferation of different L2 solutions, each with its own unique design and implementation, can lead to fragmentation and interoperability challenges within the Bitcoin ecosystem. Users may find it difficult to move assets and data between different L2s, hindering the ability to compose and combine various applications and services seamlessly.
Lack of interoperability can lead to liquidity fragmentation, where assets and user activity are spread across multiple, siloed L2 solutions. This fragmentation can reduce network effects, limit the potential for innovation, and create a suboptimal user experience, similar to what the Ethereum ecosystem has experienced with its numerous L2s.
To address these challenges and drawbacks, developers and the Bitcoin community must prioritize user experience, decentralization, and interoperability when designing and implementing L2 solutions. By focusing on usability, minimizing trust assumptions, and promoting standards for cross-layer interoperability, the ecosystem can work towards overcoming these hurdles and realizing the full potential of Bitcoin L2s.
It is important to recognize that the development of L2 solutions is still in its early stages, and many of these challenges are actively being addressed. As the ecosystem matures and best practices emerge, we can expect to see further refinements and innovations that tackle these issues head-on, ultimately leading to a more robust, accessible, and composable Bitcoin L2 landscape.
The Future of Bitcoin L2s:
Bitcoin L2s have the potential to achieve what Ethereum L2s cannot – tap into Bitcoin's unparalleled liquidity, market dominance, security, decentralization, and network effects. Among the EVM-based Bitcoin L2s mentioned in the article, Merlin Chain appears to have the highest chance of success due to its strong technical foundation, which leverages Polygon's zkEVM and a decentralized oracle to inherit Bitcoin's security. Its scalability, privacy features, on-chain fraud proof modules, and unique account abstraction model, combined with the strong backing and ecosystem support from the team behind the successful Ordinals project and prominent investors, position Merlin Chain as a promising contender in the race to bridge the Bitcoin and Ethereum ecosystems.
As Bitcoin L2s continue to evolve, they are poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of decentralized finance (DeFi). With Bitcoin's market dominance of over 50% and a community of over 100 million BTC holders, protocols building on top of Bitcoin have a rare opportunity to rapidly grow their user base through successful marketing campaigns.
With institutions holding over 8% of the total Bitcoin supply, those seeking to earn additional yield to outperform others may look to Bitcoin L2s. Once institutional-grade custody and wallet solutions like Fireblocks integrate with Bitcoin L2s, there could be more institutional adoption, and Bitcoin L2s may become the preferred platform for institutional-grade DeFi applications and services. A significant game-changing event, and in my opinion, an inevitability, would be the integration of native USDC on Bitcoin L2s. Currently, projects like Stacks rely on bridged USDC via protocols like Allbridge. Native USDC would attract institutional players seeking regulatory compliance and familiarity with fiat-backed stablecoins. This development could mirror the impact of native USDC on the Cosmos ecosystem, where the launch of Noble protocol's USDC integration saw the TVL in Cosmos DeFi surge from $50m to over $300m within six months.
According to data from Crypto.com, the total value locked (TVL) in Bitcoin L2s has grown from $1.2 million in January 2022 to over $200 million as of March 2023, indicating the growing interest and adoption of these solutions. It is easy to see this number continue to grow when compared to the growth of Ethereum L2s as Bitcoin L2s advances.
By combining the strength of Bitcoin's base layer with the scalability, programmability, and flexibility of L2s, we may be witnessing the very emergence of a truly decentralized and inclusive financial ecosystem that empowers individuals and institutions alike.
As Bitcoin L2s usher in a new era of decentralized finance, will they be the catalyst that propels Bitcoin from digital gold to the backbone of the global financial system?
Disclaimer
The Blockcrunch Podcast (“Blockcrunch”) is an educational resource intended for informational purposes only. Blockcrunch produces a weekly podcast and newsletter that routinely covers projects in Web 3 and may discuss assets that the host or its guests have financial exposure to.
Some Blockcrunch VIP posts are written by contractors to Blockcrunch and posts reflect the contractors’ independent views, not Blockcrunch’s official stance. Blockcrunch requires contractors to disclose their financial exposure to projects they write about but is not able to fully guarantee no such conflicts of interest exist. Blockcrunch itself will not buy or sell assets it covers 72 hours prior to and subsequent to the publication of a piece; however, its directors, employees, contractors and affiliates may buy or sell assets prior to or subsequent to publication of any content and will make disclosures on a best effort basis.
Views held by Blockcrunch’s guests are their own. None of Blockcrunch, its registered entity or any of its affiliated personnel are licensed to provide any type of financial advice, and nothing on Blockcrunch’s podcast, newsletter, website and social media should be construed as financial advice. Blockcrunch also receives compensation from its sponsor; sponsorship messages do not constitute financial advice or endorsement.
For more detailed disclaimers, visit https://blockcrunch.substack.com/about